Causal Agent:
Fungus (Sclerotium rolfsii)
| Characteristic Symptoms: | |
 |
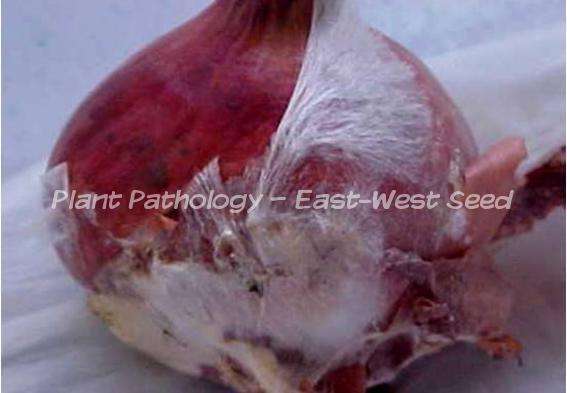
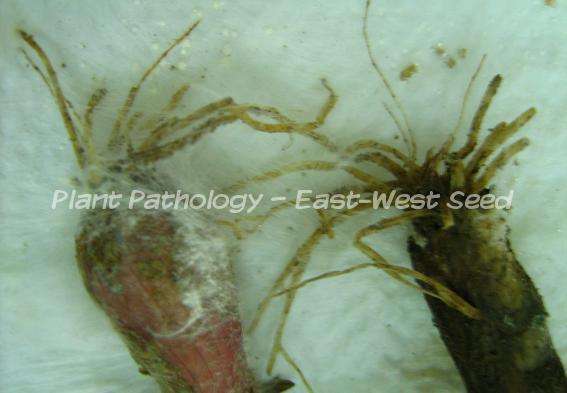
Affected onion bulb are usually covered with web of white mycelia with brown to black "sclerotial bodies".
|
 |
Bulb size is reduced and eventually becomes rot. |
| Conditions for Disease Development: | |
 |
The disease is favored by high soil moisture and high temperature. |
 |
The fungus survives in soil and crop residues for long periods of time in the form of sclerotia which be a new source of infection. |
| Management and Control: | |
 |
Crop rotation (e.g. corn) and soil solarization, deep plowing and flooding may help reduce the inoculum in the soil.
|
 |
Restriction of movement of equipment and planting materials can help minimize spread and/or avoid introduction of this disease. |
 |
Spray with chemical fungicides like difenoconazole (e.g. ScoreⓇ, MontanaⓇ, PursueⓇ, BashⓇ), Pyraclostrobin (e.g. Cabrio 25 ECⓇ), metalaxyl+mancozeb (e.g. Ridomil Gold MZ 68 WGⓇ, Apron XL 350 ESⓇ) or carbendazim ( (Bavistin 50 DFⓇ, Goldazim 500 SSⓇ, Minx 500 SCⓇ, SuperdazimⓇ, Avert 50 WPⓇ, BiostinⓇ) to minimize infection. |
 |
Soak bulbs in fungicide after harvesting to prevent bulb rotting during storage.
|
To view other diseases, click here.
Need more help? Ask the Doctor.